Design resilient microservices in Golang
If your company, like mine, implements the microservice architecture, it is designed so that one microservice calls another. In case if one service experiencing failure all upstreams of that service receive the same error. Problems in one service affect all upstreams, the nightmare of any engineer 🔥.
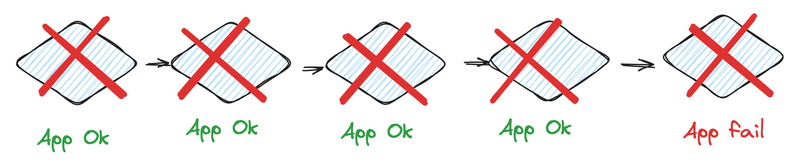
Let me explain it with a few simple diagrams. There is the bookstore an application where you can get some information about books, the booksvc, and the storagesvc provide that information.
The simple diagram below reflect how usually services in a bound context work.
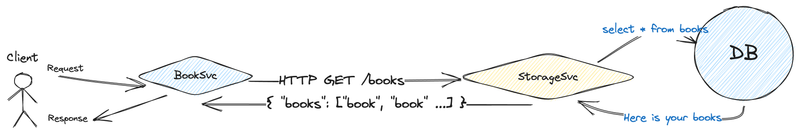
- Client (any kind of client like web, ios or android application) sends a request, it passthrough
booksvcand reachesstoragesvc. - The
storagesvcrequest the database. storagesvcprocesses data and returns it to thebooksvc.
Everything is good, so far 😻.
Now imagine something happens with the database. The database becomes unavailable. That situation is urgent. Our bookstore is unable to provide any service. The client receives errors continuously.
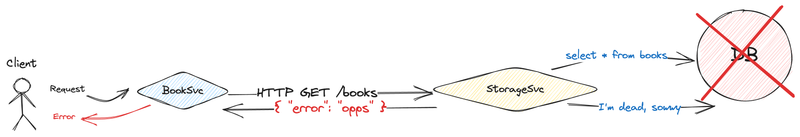
A good engineer can predict that kind of situation and use different patterns to avoid things like this. I will show you a few patterns, those patterns can be used separately or all together it depends on the particular application requirements.
Jump to #
Code #
We need some testing stage, lets create one:
mkdir -p circuitbreakercd circuitbreaker- create files
docker-compose.yaml,Dockerfile.booksvc,Dockerfile.storagesvc,pkg/recache/recache.go,storagesvc.go,go.mod
services:
database:
image: postgres:12.8
restart: always
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=pg
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=pass
- POSTGRES_DB=crud
ports:
- 5432:5432
networks:
- "test_network"
redis:
image: 'bitnami/redis:latest'
environment:
- ALLOW_EMPTY_PASSWORD=yes
networks:
- "test_network"
booksvc:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: ./Dockerfile.booksvc
ports:
- "8081:8081"
environment:
REDIS_ADDR: redis:6379
HTTP_PORT: ":8081"
depends_on:
- redis
- database
networks:
- "test_network"
storagesvc:
build:
context: .
dockerfile: ./Dockerfile.storagesvc
environment:
HTTP_PORT: ":8082"
depends_on:
- booksvc
networks:
- "test_network"
networks:
test_network:
driver: bridgeFROM golang:1.21
RUN mkdir /app
COPY . /app
WORKDIR /app
RUN go mod download
RUN go build -o booksvc booksvc.go
CMD "/app/booksvc"FROM golang:1.21
RUN mkdir /app
COPY . /app
WORKDIR /app
RUN go mod download
RUN go build -o storagesvc storagesvc.go
CMD "/app/storagesvc"package recache
import (
"time"
rds "github.com/redis/go-redis/v9"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
)
type Redis interface {
Get(ctx context.Context, key string) (string, error)
Put(ctx context.Context, key string, value interface{}) error
}
type service struct {
c *rds.Client
}
func New(options *rds.Options) Redis {
redisClient := rds.NewClient(options)
return &service{c: redisClient}
}
func (s *service) Get(ctx context.Context, key string) (string, error) {
status := s.c.Get(ctx, key)
return status.Result()
}
func (s *service) Put(ctx context.Context, key string, value interface{}) error {
status := s.c.Set(ctx, key, value, time.Minute*10)
return status.Err()
}package main
import (
"log"
"log/slog"
"net/http"
"os"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
"gorm.io/driver/postgres"
"gorm.io/gorm"
)
var (
logger = slog.New(slog.NewJSONHandler(os.Stdout, &slog.HandlerOptions{}).WithAttrs([]slog.Attr{slog.String("app", "storagesvc")}))
)
type book struct {
Id int `json:"id" gorm:"primaryKey"`
Title string `json:"title"`
Author string `json:"author"`
Desc string `json:"desc"`
}
func main() {
// Echo instance
e := echo.New()
db, err := gorm.Open(postgres.Open("postgres://pg:pass@database:5432/crud"), &gorm.Config{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
}
db.AutoMigrate(&book{})
// Seed database with some data
if result := db.Create(&book{Title: "One book", Author: "John Doe"}); result.Error != nil {
logger.With("error", result.Error).Info("cant create data")
}
if result := db.Create(&book{Title: "Second book", Author: "Jane Doe"}); result.Error != nil {
logger.With("error", result.Error).Info("cant create data")
}
// Routes
e.GET("/books", func(c echo.Context) error {
var books []book
if result := db.Find(&books); result.Error != nil {
logger.With("error", result.Error).Info("cant fetch data")
return c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, map[string]interface{}{"error": "ops, I cant process you request"})
}
logger.With("got books", books).Info("data fetched")
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, books)
})
// Start server
e.Logger.Fatal(e.Start(":8082"))
}module example
go 1.21
require (
github.com/cenkalti/backoff/v4 v4.2.1
github.com/labstack/echo/v4 v4.10.2
github.com/redis/go-redis/v9 v9.0.5
github.com/sony/gobreaker v0.5.0
golang.org/x/net v0.9.0
gorm.io/driver/postgres v1.5.2
gorm.io/gorm v1.25.3
)
require (
github.com/cespare/xxhash/v2 v2.2.0 // indirect
github.com/dgryski/go-rendezvous v0.0.0-20200823014737-9f7001d12a5f // indirect
github.com/jackc/pgpassfile v1.0.0 // indirect
github.com/jackc/pgservicefile v0.0.0-20221227161230-091c0ba34f0a // indirect
github.com/jackc/pgx/v5 v5.3.1 // indirect
github.com/jinzhu/inflection v1.0.0 // indirect
github.com/jinzhu/now v1.1.5 // indirect
github.com/labstack/gommon v0.4.0 // indirect
github.com/mattn/go-colorable v0.1.13 // indirect
github.com/mattn/go-isatty v0.0.17 // indirect
github.com/valyala/bytebufferpool v1.0.0 // indirect
github.com/valyala/fasttemplate v1.2.2 // indirect
golang.org/x/crypto v0.8.0 // indirect
golang.org/x/sys v0.7.0 // indirect
golang.org/x/text v0.9.0 // indirect
)Retry #
Let's start with a simple one, the Retry.
We introduce the Retry logic in our booksvc, so the service will exponentially repeat a request to storagesvc while the client waits.
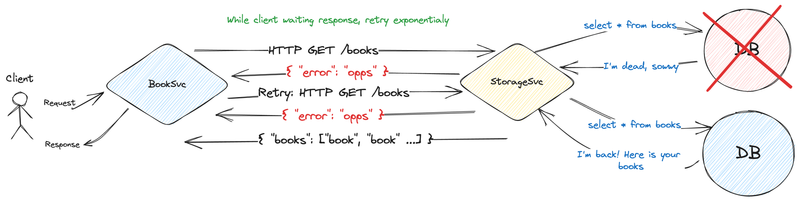
If our database fails to serve queries booksvc will wait and try again and again.
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"io/ioutil"
"log/slog"
"net/http"
"os"
"example/pkg/recache"
. "github.com/cenkalti/backoff/v4"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
rds "github.com/redis/go-redis/v9"
)
var (
storagesvc = "http://storagesvc:8082/books"
cacheKey = "item"
logger = slog.New(
slog.NewJSONHandler(os.Stdout, &slog.HandlerOptions{}).WithAttrs([]slog.Attr{slog.String("app", "booksvc")}),
)
)
type svc struct {
storageSvcPath string
cache recache.Redis
httpClient *http.Client
}
// DefaultInitialInterval = 500 * time.Millisecond
// DefaultRandomizationFactor = 0.5
// DefaultMultiplier = 1.5
// DefaultMaxInterval = 60 * time.Second
// DefaultMaxElapsedTime = 15 * time.Minute
func main() {
// Echo instance
e := echo.New()
// Initialize storage service
storageSvc := svc{
storageSvcPath: storagesvc,
httpClient: &http.Client{},
cache: recache.New(&rds.Options{
Addr: "redis:6379",
DB: 0,
}),
}
// Routes
e.GET("/", storageSvc.mainHandler)
// Start server
e.Logger.Fatal(e.Start(":8081"))
}
// Root HTTP Handler of booksvc
func (s *svc) mainHandler(c echo.Context) error {
var (
err error
books []interface{}
)
// Operation to retry
// here we retry our request
operation := func() error {
logger.Info("client: get books")
books, err = s.getBooks()
if err != nil {
logger.With("error", err).Error("client: error")
return err
}
return nil
}
// Actual retry call, if at the end retry fail we return an error
if err = Retry(operation, NewExponentialBackOff()); err != nil {
logger.With("error", err).Error("client: error")
return c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, map[string]interface{}{"error": "ops, I cant process you request"})
}
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, books)
}
// Call storagesvc
func (s *svc) getBooks() ([]interface{}, error) {
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, s.storageSvcPath, nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
res, err := s.httpClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if res.StatusCode == http.StatusInternalServerError {
return nil, errors.New("bad response code")
}
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
var books []interface{}
json.Unmarshal(body, &books)
return books, nil
}Stop the database container docker stop circutbreaker-database-1 and check by querying the booksvc with curl -s http://localhost:8081/. You'll see curl hangs and requests to storagesvc continuously repeated in the logs.
Circuit Breaker #
Now the circuit breaker
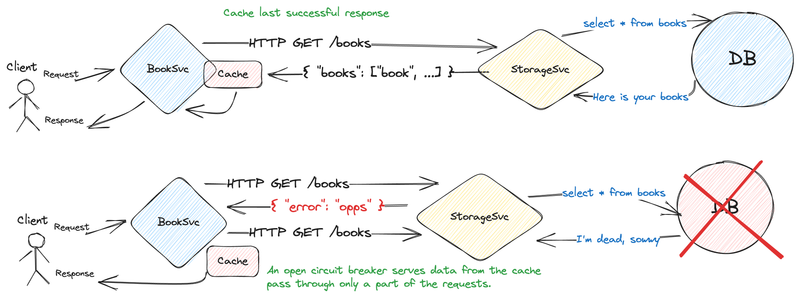
That pattern we'll use with Redis cache, in the booksvc, we add the circuit breaker. Our cache will store the last successful request to storagesvc, and if the circuit breaker persists in an open state, we serve the data from the cache.
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"io/ioutil"
"log/slog"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
"example/pkg/recache"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
rds "github.com/redis/go-redis/v9"
"github.com/sony/gobreaker"
)
var (
storagesvc = "http://storagesvc:8082/books"
cacheKey = "item"
logger = slog.New(
slog.NewTextHandler(os.Stdout, &slog.HandlerOptions{}).WithAttrs([]slog.Attr{slog.String("app", "booksvc")}),
)
cb *gobreaker.CircuitBreaker
)
type svc struct {
storageSvcPath string
cache recache.Redis
httpClient *http.Client
}
func init() {
var st gobreaker.Settings
st.Name = "HTTP GET"
st.Timeout = time.Second * 5
st.Interval = time.Second * 10
st.ReadyToTrip = func(counts gobreaker.Counts) bool {
return counts.ConsecutiveFailures > 0
}
cb = gobreaker.NewCircuitBreaker(st)
}
func main() {
// Echo instance
e := echo.New()
// Initialize storage service
storageSvc := svc{
storageSvcPath: storagesvc,
httpClient: &http.Client{},
cache: recache.New(&rds.Options{
Addr: "redis:6379",
DB: 0,
}),
}
// Routes
e.GET("/", storageSvc.mainHandler)
// Start server
e.Logger.Fatal(e.Start(":8081"))
}
// Root HTTP Handler
func (s *svc) mainHandler(c echo.Context) error {
var (
err error
data []interface{}
)
data, err = cb.Execute(s.getBooks)
if err != nil {
// If circuit breaker in the open state
// serve last successful request from out cache
if errors.Is(err, gobreaker.ErrOpenState) {
item, _ := s.cache.Get(context.Background(), cacheKey)
var m []interface{}
json.Unmarshal([]byte(item), &m)
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, m)
}
logger.With("error", err).Error("client: error")
return c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, map[string]interface{}{"error": "ops, I cant process you request"})
}
logger.Info("client: got response")
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, data)
}
// Storage Service
func (s *svc) getBooks() ([]interface{}, error) {
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, s.storageSvcPath, nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
res, err := s.httpClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if res.StatusCode == http.StatusInternalServerError {
return nil, errors.New("bad response code")
}
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
// Put last successfull request to the cache
go s.cache.Put(context.Background(), cacheKey, string(body))
var books []interface{}
json.Unmarshal(body, &books)
return books, nil
}Stop the database container docker stop circutbreaker-database-1 and check by querying the booksvc with curl -s http://localhost:8081/. Half of the requests to storagesvc fail, and the second half is returned from the cache.
All things together #
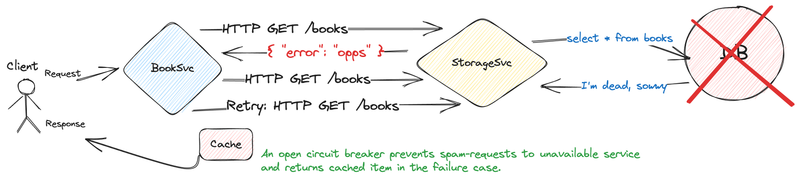
The last one is Retry with the circuit breaker in this case, our client shouldn't receive any errors and circuit breaker prevents retry from spamming our storagesvc continuously.
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"io/ioutil"
"log/slog"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
"example/pkg/recache"
. "github.com/cenkalti/backoff/v4"
"github.com/labstack/echo/v4"
rds "github.com/redis/go-redis/v9"
"github.com/sony/gobreaker"
)
var (
storagesvc = "http://storagesvc:8082/books"
cacheKey = "item"
logger = slog.New(
slog.NewTextHandler(os.Stdout, &slog.HandlerOptions{}).WithAttrs([]slog.Attr{slog.String("app", "booksvc")}),
)
cb *gobreaker.CircuitBreaker
badResponseErr = errors.New("bad response code")
maxRetries = uint64(7)
)
type svc struct {
storageSvcPath string
cache recache.Redis
httpClient *http.Client
}
func init() {
var st gobreaker.Settings
st.Name = "HTTP GET"
st.Timeout = time.Second * 5
st.Interval = time.Second * 10
st.ReadyToTrip = func(counts gobreaker.Counts) bool {
return counts.ConsecutiveFailures > 0
}
cb = gobreaker.NewCircuitBreaker(st)
}
func main() {
// Echo instance
e := echo.New()
// Initialize storage service
storageSvc := svc{
storageSvcPath: storagesvc,
httpClient: &http.Client{},
cache: recache.New(&rds.Options{
Addr: "redis:6379",
DB: 0,
}),
}
// Routes
e.GET("/", storageSvc.mainHandler)
// Start server
e.Logger.Fatal(e.Start(":8081"))
}
// Root HTTP Handler
func (s *svc) mainHandler(c echo.Context) error {
var (
err error
data []interface{}
)
// Operation to retry
operation := func() error {
data, err = cb.Execute(s.getBooks)
if err != nil {
logger.Error("client: error", "error", err)
return err
}
return nil
}
if err := Retry(operation, WithMaxRetries(NewExponentialBackOff(), maxRetries)); err != nil {
// If max retry count exceed we get data from cache
item, _ := s.cache.Get(context.Background(), cacheKey)
var m []interface{}
json.Unmarshal([]byte(item), &m)
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, m)
}
if data != nil {
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, data)
}
return c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, map[string]interface{}{"error": "ops, I cant process you request"})
}
// Storage Service
func (s *svc) getBooks() ([]interface{}, error) {
req, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodGet, s.storageSvcPath, nil)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
res, err := s.httpClient.Do(req)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if res.StatusCode == http.StatusInternalServerError {
return nil, badResponseErr
}
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
go s.cache.Put(context.Background(), cacheKey, string(body))
var books []interface{}
json.Unmarshal(body, &books)
return books, nil
}Stop the database container docker stop circutbreaker-database-1 and check by querying the booksvc with curl -s http://localhost:8081/. The request will probably hang for a while but it soon returns a cached response and it shouldn't return any errors in all next requests.
Conclusion #
The patterns I've described help you design and implement resilient microservice and limit the impact of service failures and latencies. That code must be used with proper alerting so you can understand fastly what goes wrong and fix it.
Credits #
- backoff - The exponential backoff algorithm in Go
- gobreaker - Circuit Breaker implemented in Go
- This article is a Golang version of
Cache , retry or breakwith some changes.
Happy coding!