Organize gRPC and protobuf code in Golang
In this article, I'll describe how to organize protobuf files messages and gRPC services in the Go sources. I'll briefly examine how to use protoc and plugins with the proper imports, and project structure.
Requirements:
Go>= 1.21Docker,docker-compose
A diagram describes how the repositories service-a, service-b requires echo-contracts:
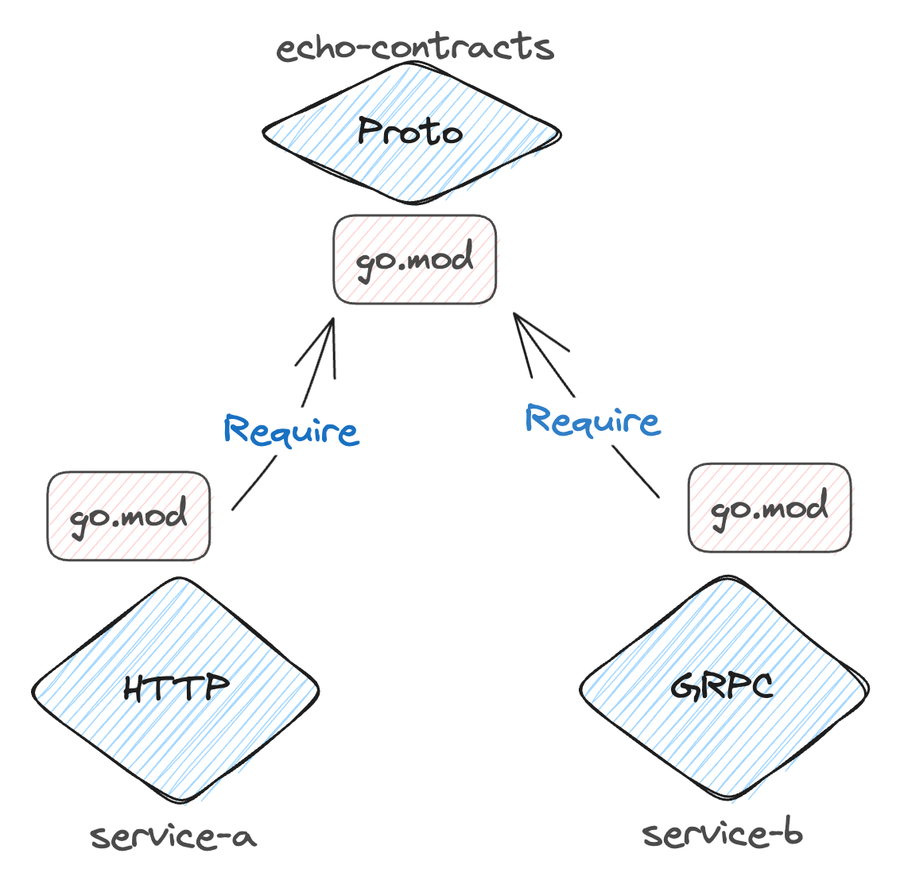
Jumt to #
Project structure #
The repository echo-contracts describes our proto files. It is a standalone Go repository intended to import into other Go sources. Below is a project structure:
├── Makefile
├── docker
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── docker-compose.yaml
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
└── pb
├── message.proto
└── service.protoMakefile #
The Makefile contains a bunch of valuable targets.
PROTOC_VERSION ?= 24.0
.PHONY: help
help: ## Display available commands.
@awk 'BEGIN {FS = ":.*?## "} /^[a-zA-Z_-]+:.*?## / {printf "\033[36m%-30s\033[0m %s\n", $$1, $$2}' $(MAKEFILE_LIST)
.PHONY: proto-clean
proto-clean: ## Clean generated proto.
@rm -rf pb/message
@rm -rf pb/service
.PHONY: proto-compile
proto-compile: ## Compile message protobuf and gRPC service files.
PLATFORM=$(shell uname -m) PROTOC_VERSION=$(PROTOC_VERSION) docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yaml run --rm protogen
.PHONY: docker-config
docker-config: ## Dump docker-compose configuration.
PLATFORM=$(shell uname -m) PROTOC_VERSION=$(PROTOC_VERSION) docker-compose -f docker/docker-compose.yaml configDockerfile #
In the Dockerfile, protoc with a particular version is downloaded. The version of protoc binary is declared as PROTOC_VERSION variable at the top of the Makefile and is passed to the docker container during the build stage.
protoc doesn't officially support Go as output, you need to install external plugins.
gRPC is not the same as Protocol Buffers, gRPC uses Protocol Buffers, hence different plugins are needed to generate Go code messages and services.
Plugins installed:
- protoc-gen-go-grpc - Generates
Gobindings of services in protobuf definition files forgRPC. - protoc-gen-go - A tool to generate
Gocode for the protocol buffer language, and also the runtime implementation to handle serialization of messages inGo.
FROM golang:1.21
ARG PLATFORM
ARG PROTOC_VERSION
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y unzip
# By default Intel chipset (x86_64) is assumed but if the host device is an Apple
# silicon (arm) chipset based then a relevant (aarch_64) release file is used.
RUN go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/[email protected]
RUN go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/[email protected]
RUN export ZIP=x86_64 && \
if [ ${PLATFORM} = "arm64" ]; then export ZIP=aarch_64; fi && \
wget --quiet https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v${PROTOC_VERSION}/protoc-${PROTOC_VERSION}-linux-${ZIP}.zip && \
unzip -o protoc-${PROTOC_VERSION}-linux-${ZIP}.zip -d /usr/local bin/protoc && \
unzip -o protoc-${PROTOC_VERSION}-linux-${ZIP}.zip -d /usr/local 'include/*'docker-compose #
I'm using docker-compose.yaml as an engine for generating proto.
services:
protogen:
build:
context: "."
args:
PLATFORM: ${PLATFORM}
PROTOC_VERSION: ${PROTOC_VERSION}
working_dir: "/source"
volumes:
- "../pb:/source"
command: bash -c "
protoc *.proto --proto_path=.
--go_out=. --go_opt=module=github.com/user/echo-contracts/pb
--go-grpc_out=. --go-grpc_opt=module=github.com/user/echo-contracts/pb
"proto options #
Now we're instructing the protoc to generate code for us, we're planning to import echo-contracts as Go module and we need a proper package structure.
There is an options for --go_out and --go-grpc_opt:
module=$PREFIX- the output file is placed in a directory named after theGopackage’s import path, but with the specified directory prefix removed from the output filename.
For example, an input file pb/message.proto with a Go import path of github.com/user/echo-contracts/pb/message and github.com/user/echo-contracts/pb specified as the module prefix results in an output file at pb/message/message.pb.go.
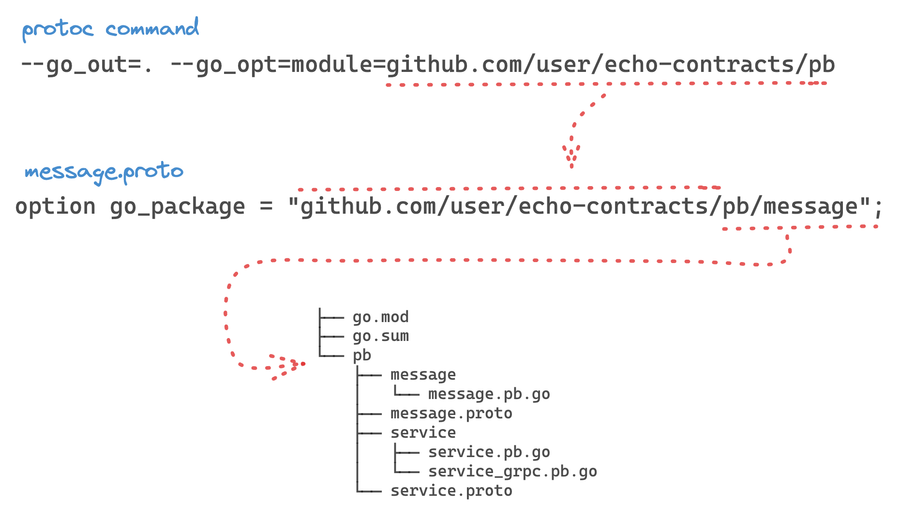
Here are our proto files:
syntax = "proto3";
package echo.service.v1;
option go_package = "github.com/user/echo-contracts/pb/message";
message StringMessage {
string value = 1;
}syntax = "proto3";
package echo.service.v1;
option go_package = "github.com/user/echo-contracts/pb/service";
import "message.proto";
service EchoService {
rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {}
}module github.com/user/echo-contracts
go 1.21.0
require (
google.golang.org/grpc v1.57.0
google.golang.org/protobuf v1.31.0
)
require (
github.com/golang/protobuf v1.5.3 // indirect
golang.org/x/net v0.9.0 // indirect
golang.org/x/sys v0.7.0 // indirect
golang.org/x/text v0.9.0 // indirect
google.golang.org/genproto/googleapis/rpc v0.0.0-20230525234030-28d5490b6b19 // indirect
)generate #
At this step we can generate Go code from proto files. Use the command make proto-compile.
Here is the directory structure after proto compilation:
├── Makefile
├── docker
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── docker-compose.yaml
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
└── pb
├── message
│ └── message.pb.go
├── message.proto
├── service
│ ├── service.pb.go
│ └── service_grpc.pb.go
└── service.protoRelease echo-contracts Using Go Modules, so it is published as Go module with the proper version.
usage #
To import our echo-contracts Go module, we need to declare it in the main.go file and go.mod as an external dependency:
package main
import (
// ...
message "github.com/user/echo-contracts/pb/message"
service "github.com/user/echo-contracts/pb/service"
// ...
)
// Some code hereAnd in go.mod:
module service-a
go 1.21.0
require (
// Some imports here
github.com/user/echo-contracts v0.0.1
)Happy coding!