Development On Apple Silicon with UTM
In this article, I'll show you how to use UTM VMs virtual machines to create Linux development environments on Apple Silicon.
This approach builds on the technique I described in here.
Dependencies #
First, install UTM using Homebrew: brew install --cask utm.
Then, install brew install cdrtools, which provides mkisofs. We'll use that tool to create an init.iso - our seed script for initializing the VM.
We need a bunch of tools and images.
-
Fedora Cloud images mirror.bahnhof.net.
-
Ubuntu Cloud images cdimage.ubuntu.com.
Cloud-Init #
We’ll use cloud-init scripts to bootstrap the VM with the tools and settings needed for development - things like git, jq, go, docker, and more. We'll also use it to provision an SSH key for easy access.
#cloud-config
system_info:
default_user:
name: fedora
users:
- name: fedora
sudo: ['ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL']
groups: users, admin, docker
shell: /bin/bash
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ssh-rsa AAAAB3Nza...
groups:
- docker
packages:
- curl
- wget
- git
- jq
- gcc
- clang
chpasswd:
list: |
fedora:password
expire: False
resize_rootfs: True
write_files:
- path: /etc/sysctl.d/enabled_ipv4_forwarding.conf
content: |
net.ipv4.conf.all.forwarding=1
- path: /opt/go.sh
owner: fedora:fedora
permissions: '0700'
content: |
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -ex
wget https://go.dev/dl/go1.24.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz -O go.tar.gz
sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzvf go.tar.gz
rm -rf go
echo 'export GOROOT=/usr/local/go' >> /home/fedora/.bashrc
echo 'export GOPATH=$HOME/.go' >> /home/fedora/.bashrc
echo 'export PATH=$GOPATH/bin:$GOROOT/bin:$PATH' >> /home/fedora/.bashrc
runcmd:
- [dnf, config-manager, addrepo, --from-repofile="https://download.docker.com/linux/fedora/docker-ce.repo"]
- [dnf, install, docker-ce, docker-ce-cli, containerd.io]
- [systemctl, enable, --now, docker]
- /opt/go.shGenerate init.iso (mkisofs is a part of cdrtools):
touch meta-data # going to be empty
mkisofs -output init.iso -volid cidata -joliet -rock {user-data,meta-data}Create VM #
Create VM, chose Emulate:
Chose Other:
No changes in Hardware:
Use 8GB disk, we dont need it and will remove it later.
In Summary name the VM and check Open VM Settings:
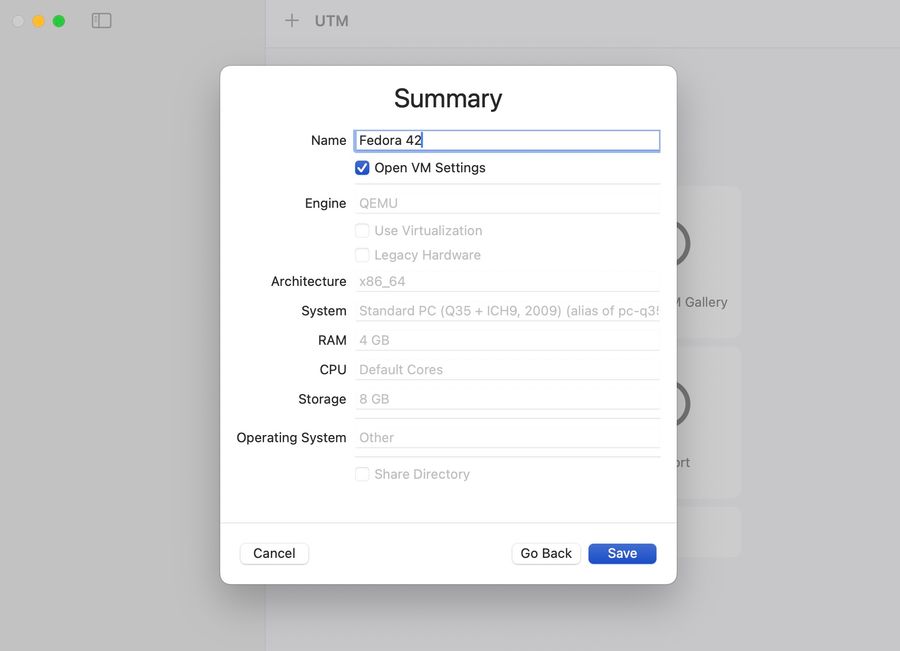
Uncheck UEFI Boot:
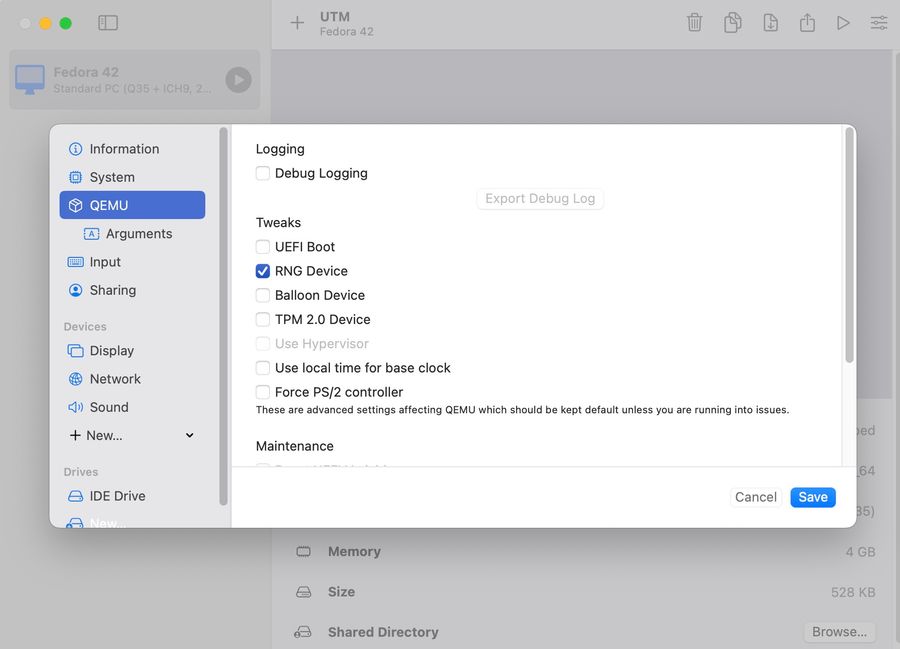
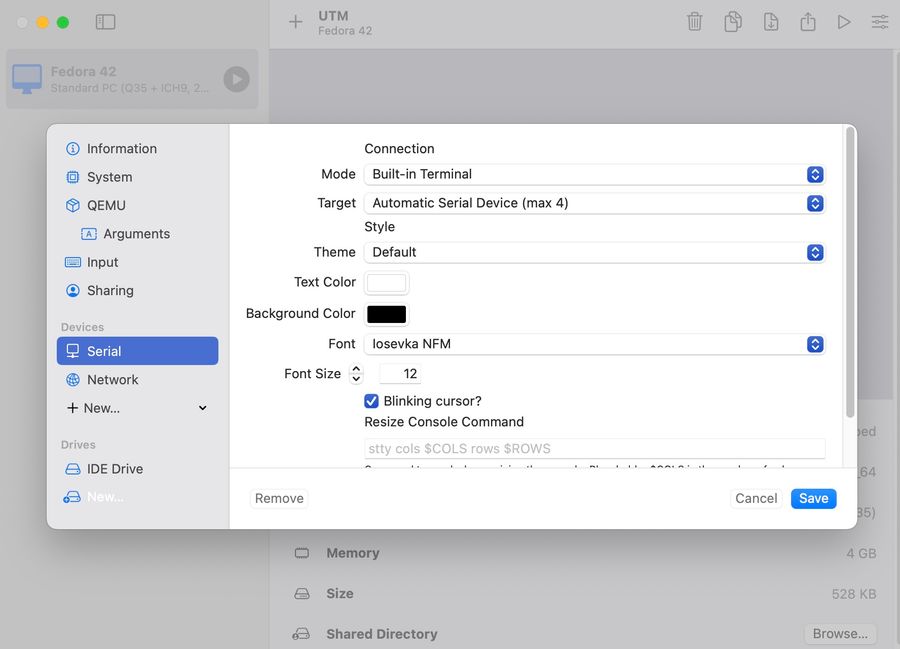
Remove Display, Sound with rigth mouse click, and add Serial -> Built-In:
Remove created Drive, and add new one VirtiO,
Import the Fedora-Cloud-Base-Generic-42-1.1.x86_64.qcow2
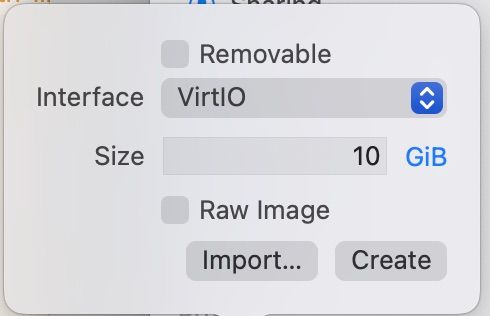
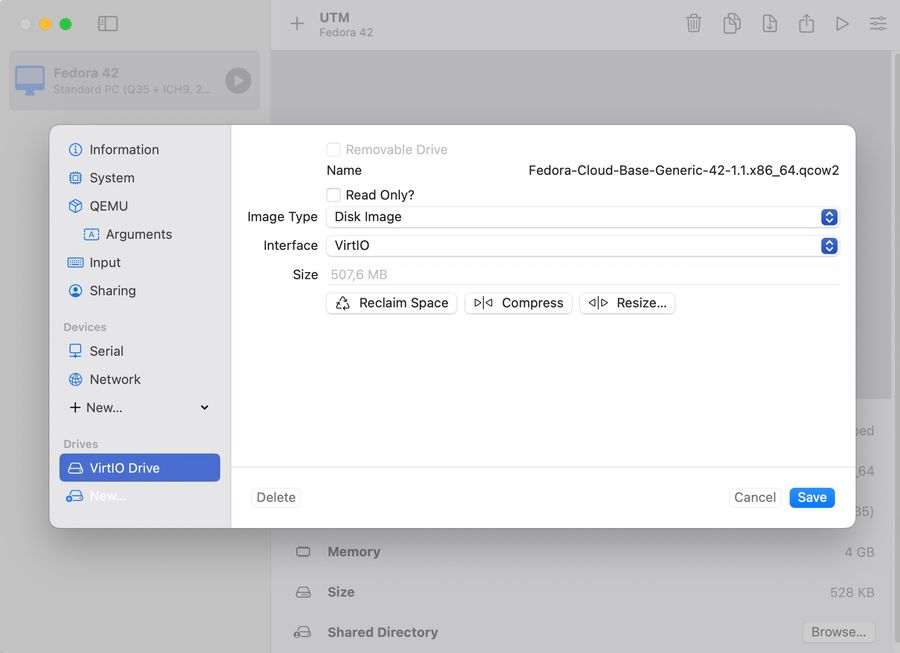
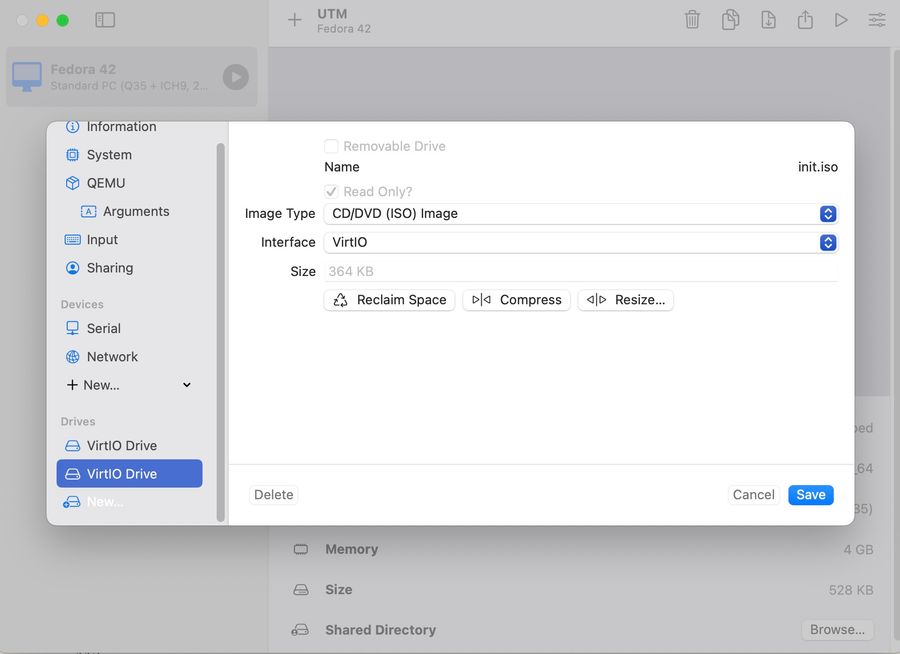
Create another one Drive -> VirtiO,
import the init.iso
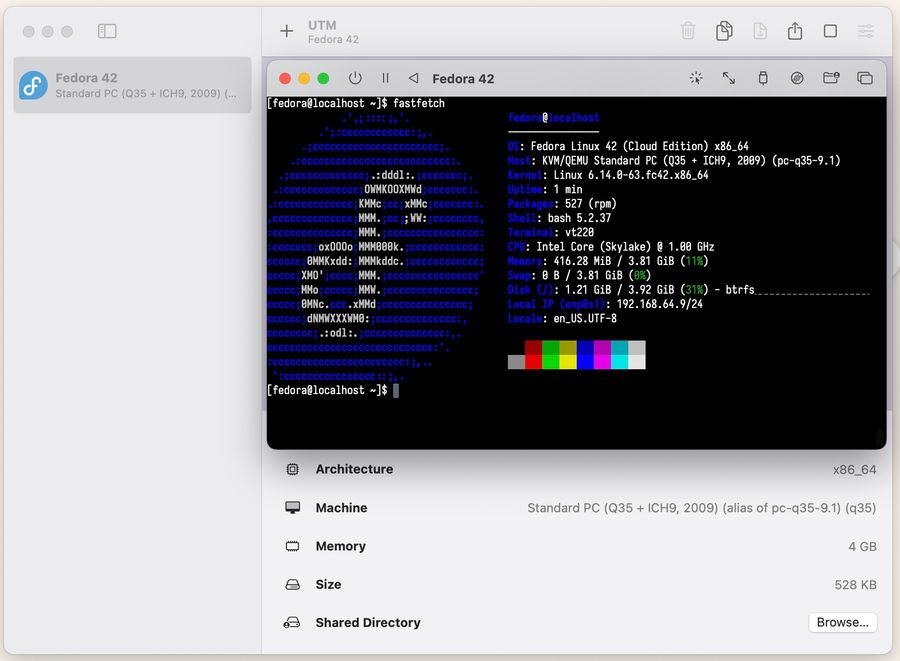
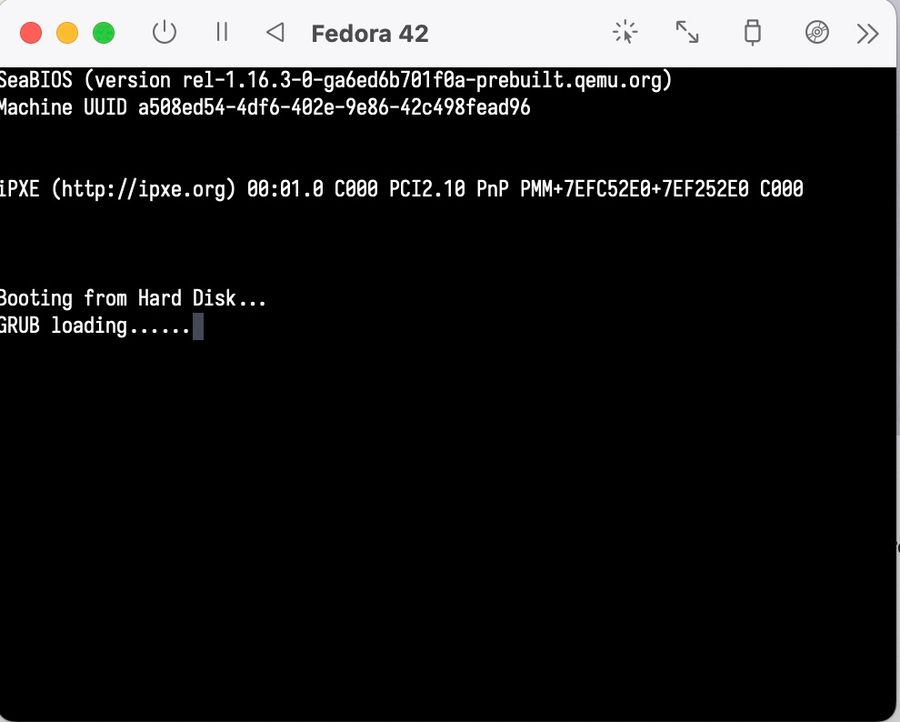
Run VM, if everything goes right you'll see boot terminal, like on the image below:
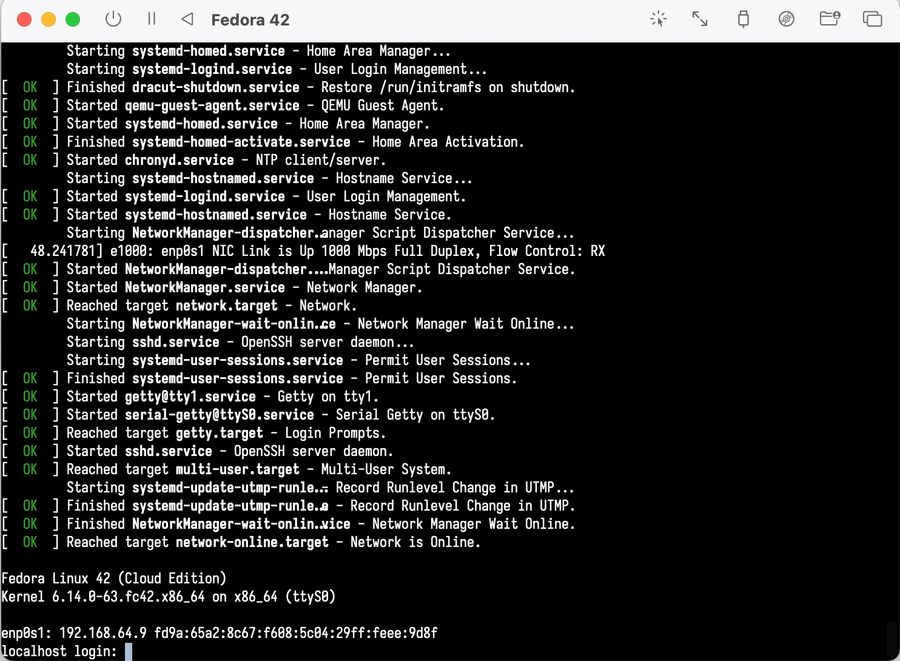
Wait until the login screen appears. The default username is fedora and the password is password, as defined in our cloud-init script.
Give it a moment after logging in cloud-init script. will need some time to finish setting everything up.
After the VM has finished initializing, power it off and remove the init.iso drive—it only needs to run during the first boot.
You can check the output of the cloud-init scripts with sudo cat /var/log/cloud-init-output.log
Tip:
To create a VM for Apple Silicon (aarch64), follow these steps:
- Choose
Virtualize, since Apple Silicon is ARM-based. - Use
arm64cloud images. - For Ubuntu, the process is almost the same - except you don’t need to disable UEFI boot.
- Don’t forget to extract the
*.img.xzfile before using it.
Happy coding!
- Previous: Use CRI-O Container Runtime with KIND